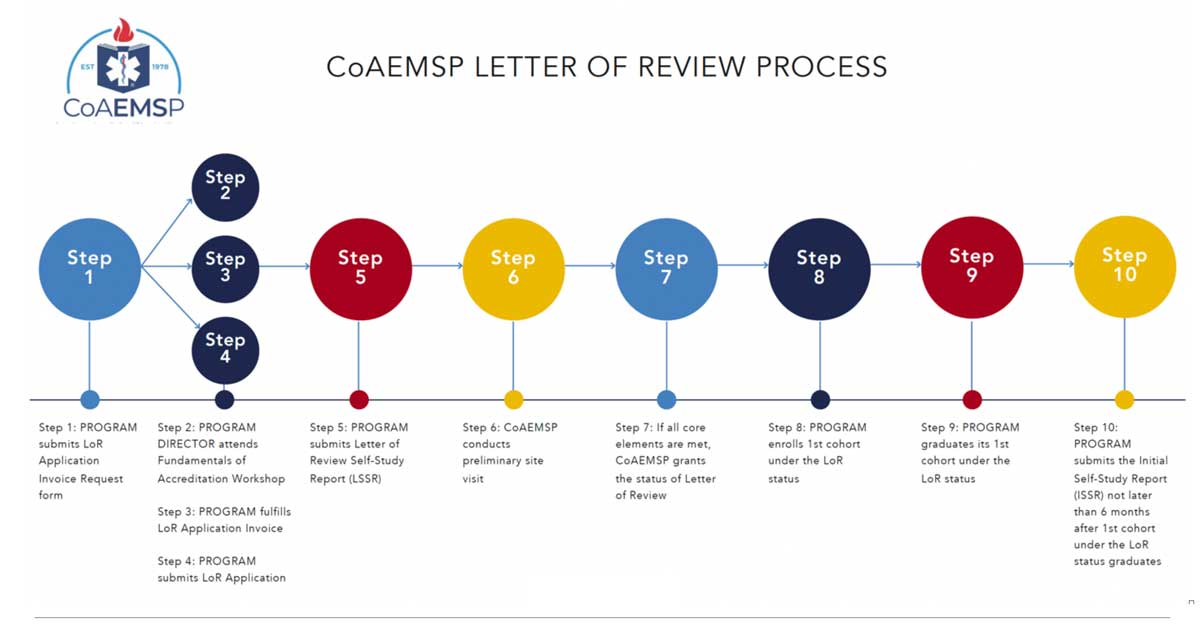
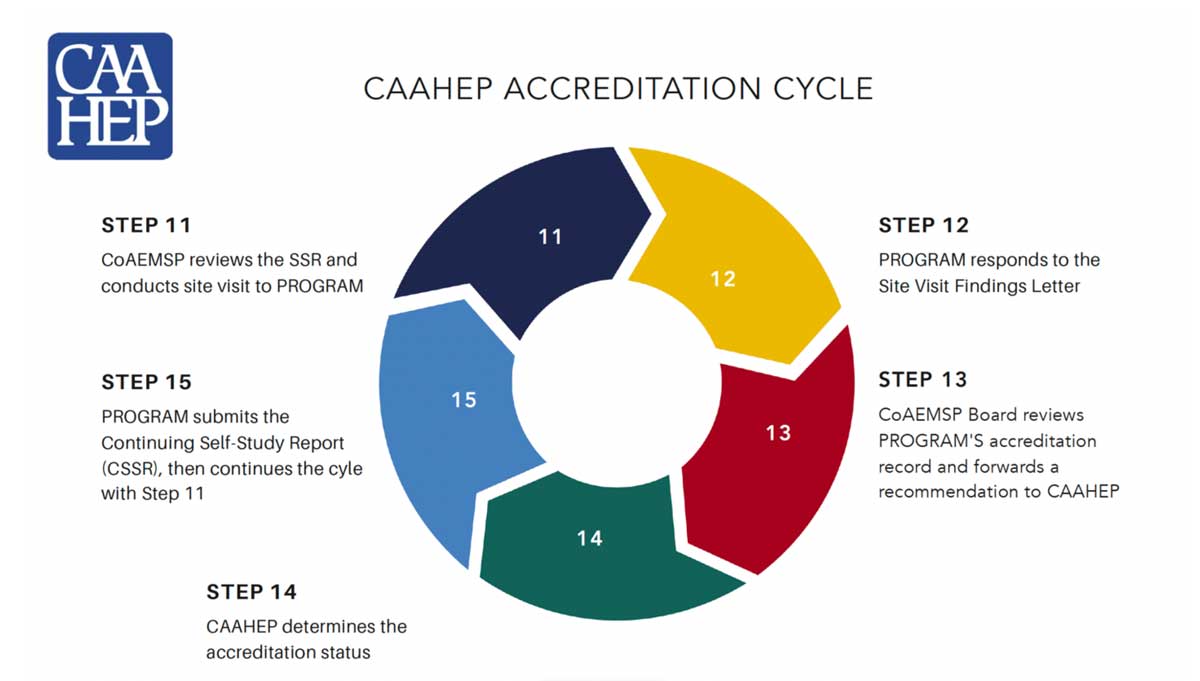
Accreditation is about quality and accountability in education.
It is “the process of formal evaluation of an educational program, institution, or system against defined standards by an external body for the purposes of quality assurance and enhancement.”
And ultimately, accreditation is about ensuring the competency of a program’s graduates. This is particularly essential in the field of healthcare professionals.
Two Kinds of Accreditation
In post-secondary education and training, there are two kinds of accreditation.
- Institutional accreditation helps to assure potential students that a school is a sound institution.
- Programmatic accreditation conducts an in-depth assessment of specialized or professional programs to ensure that the education provided meets acceptable levels of quality.
Programmatic Accreditation
Accreditors are private, nongovernmental organizations. The Committee on Accreditation of Educational Programs for the Emergency Medical Services Professions (CoAEMSP) is a not-for-profit, peer driven organization that provides the accrediting activities to AEMT and paramedic programs nationwide on behalf of the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP), the only nationally recognized accreditation organization for paramedic education.
The National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians certifies EMS clinicians, ensuring they possess the necessary competencies for safe patient care. Individual states license EMS professionals, and the Interstate Commission on EMS Personnel Practice (EMS Compact) enables licensed EMS personnel to practice in other states under specific conditions.
Resources
| Document Link | Date | Type |
|---|---|---|
| Roles & Responsibilities of Key Organizations in EMS (1-pager) | May 2025 | |
| Roles & Responsibilities of Key Organizations in EMS (full) | May 2025 |
Voluntary AEMT Accreditation starting 2025
To advance the recommendations of the 2019 National EMS Scope of Practice Model and the 2021 National EMS Education Standards, CAAHEP launched a voluntary programmatic accreditation at the Advanced Emergency Medical Technician (AEMT) level on January 1, 2025, and CoAEMSP provides the accreditation services. CAAHEP and CoAEMSP work closely with stakeholders to gather perspectives and recommendations on how best to implement the new option.
Accreditation Standards
To achieve accreditation, a paramedic education program must comply with the CAAHEP Standards and Guidelines, which include:
- Program goals that are clearly established to provide a regular assessment of learning outcomes to ensure paramedics meet minimum expectations for knowledge, skills, and behavior.
- Program resources that are sufficient to meet the established program goals, including faculty and staff, curriculum and instructional materials, computer resources, finances, facilities and equipment, and clinical affiliates.
- Student Evaluation & Assessment must be conducted on a recurrent basis and with sufficient frequency to provide both the students and program faculty with valid and timely indications of the student’s progress toward and achievement of key competencies, leading to safe clinical practice and public protection.
- Fair Practices protect the health and safety of patients, students, faculty, and other participants associated with paramedic education activities, including disclosure, nondiscriminatory, record-keeping, and other legal compliance requirements.